Tidal devices
Tidal energy exploits the natural ebb and flow of coastal tidal waters caused principally by the interaction of the gravitational fields of the earth, moon and sun. The fast sea currents are often magnified by topographical features, such as headlands, inlets and straits, or by the shape of the seabed when water is forced through narrow channels. The tidal stream devices, which utilise these currents, are broadly similar to submerged wind turbines and are used to exploit the kinetic energy in tidal currents. Due to the higher density of water, this means that the blades can be smaller and turn more slowly, but they still deliver a significant amount of power. To increase the flow and power output from the turbine, concentrators (or shrouds) may be used around the blades to streamline and concentrate the flow towards the rotors.
We have identified six main types of tidal energy converters (TECs):
A) Horizontal axis turbine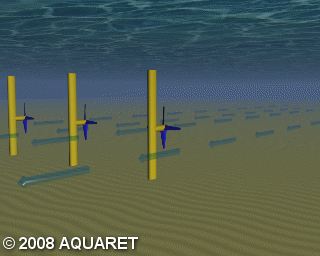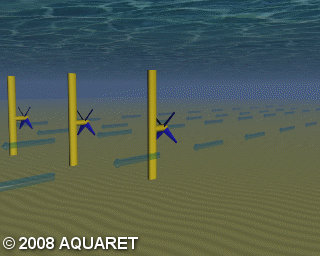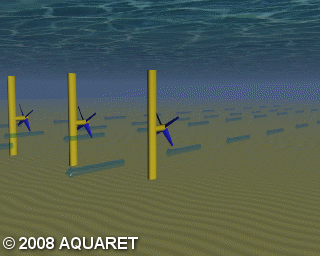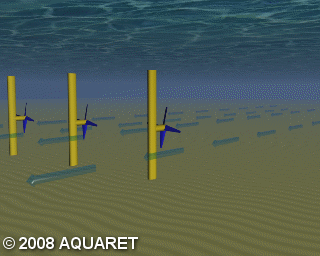
Horizontal axis turbines extract energy from moving water in much the same way as wind turbines extract energy from moving air. The tidal stream causes the rotors to rotate around the horizontal axis and generate power.
B) Vertical axis turbine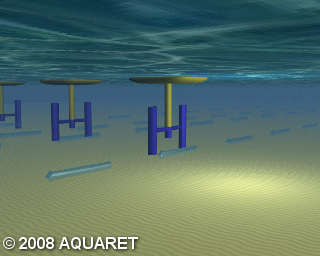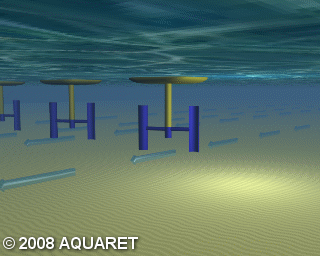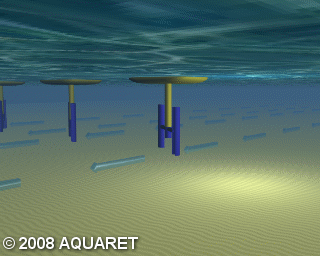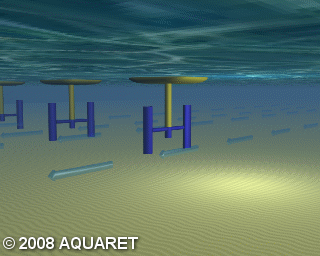
Vertical axis turbines extract energy from the tides in a similar manner to that above, however the turbine is mounted on a vertical axis. The tidal stream causes the rotors to rotate around the vertical axis and generate power.
C) Oscillating Hydrofoil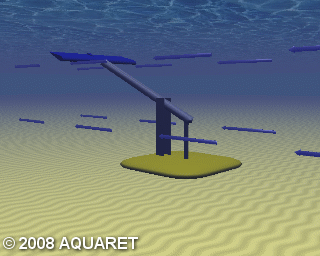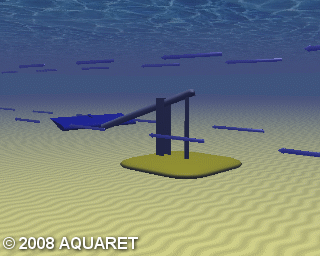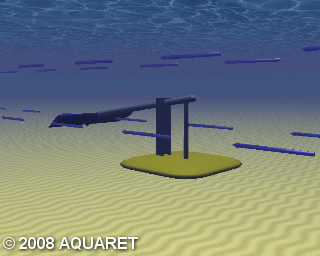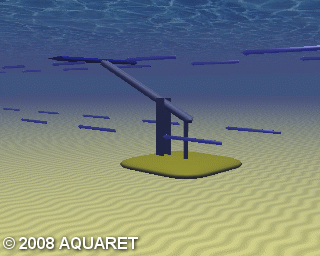
A hydrofoil is attached to an oscillating arm. The tidal current flowing either side of a wing results in lift. This motion then drives fluid in a hydraulic system to be converted into electricity.
D) Enclosed Tips (Venturi)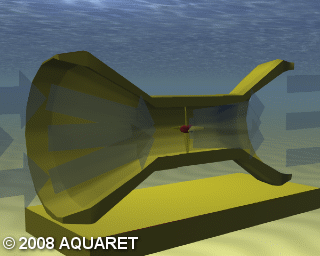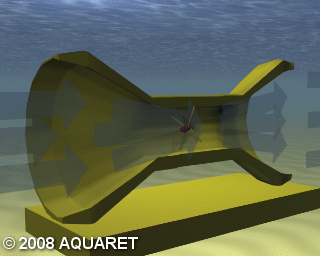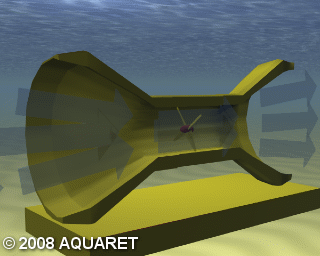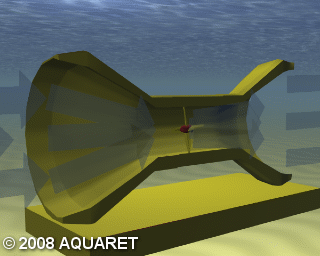
Venturi Effect devices house the device in a duct which concentrates the tidal flow passing through the turbine. The funnel-like collecting device sits submerged in the tidal current. The flow of water can drive a turbine directly or the induced pressure differential in the system can drive an air-turbine.
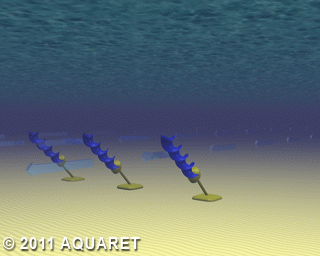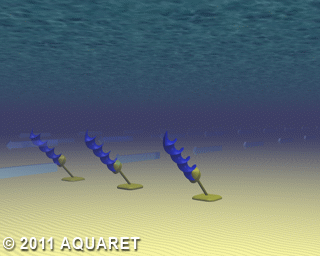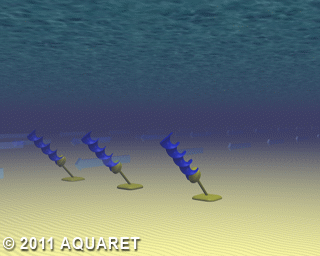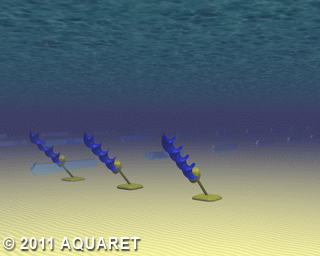
E) Archimedes Screw
The Archimedes Screw is a helical corkscrew-shaped device (a helical surface surrounding a central cylindrical shaft). The device draws power from the tidal stream as the water moves up/through the spiral turning the turbines.

F) Tidal Kite
A tidal kite is tethered to the sea bed and carries a turbine below the wing. The kite ‘flies’ in the tidal stream, swooping in a figure-of-eight shape to increase the speed of the water flowing through the turbine.
G) Other Designs
This covers those devices with a unique and very different design to the more well-established types of technology or if information on the device’s characteristics could not be determined.
To download the above animations please visit the Aqua-RET website.






