RiaSoR: Reliability in a Sea of Risk

In today’s uncertain investment environment, the perception of technical risk is dependent on how confident the investors are that ocean energy devices will perform reliably and produce the expected output from their devices. As the industry is approaching a pre-commercial stage, in-sea testing and demonstration at various scales will be a primary focus for the sector over the next three to five years. This places a key role on the ocean energy test houses to put in place a rigorous testing programme whereby the reliability of these emerging technologies can be tested and independently verified before the systems move onto large scale array deployments.
The Reliability in a Sea of Risk (RiaSoR) project addresses this strategic need, focusing on the key engineering challenges that underpin the reliability and survivability of emerging wave and tidal energy technology.
RiaSoR will establish industry best practice in reliability testing for wave and tidal devices through improved load measurements and verification, standardising design guidelines for marine energy systems, and increasing safety in marine energy operations.
For further information, visit: www.RiaSoR.eu
Oceanera-net funded
The RiaSoR project is funded by the Ocean Energy European Research Area Network (OCEANERA-NET) First Joint Call 2014, in association with Scottish Enterprise, InnovateUK and Swedish Energy Agency. For further information on OCEANERA-NET, visit: OCEANERA-NET website
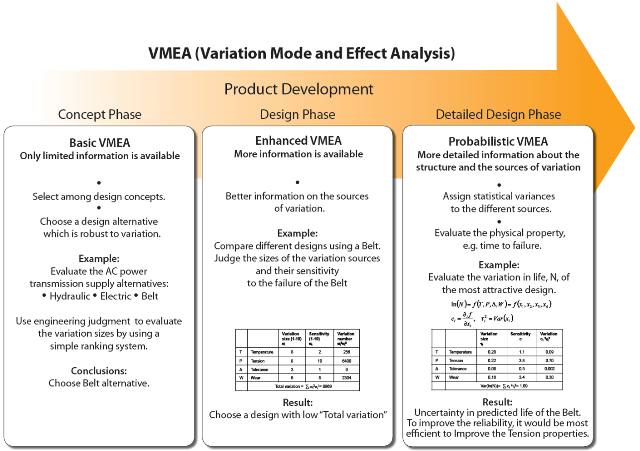
Methodology
The Variation Mode and Effect Analysis (VMEA) methodology used in other more mature sectors such as the automotive and aerospace industry will be adapted in the RiaSoR project for the ocean energy sector. VMEA is a method aimed at guiding engineers to find critical areas in terms of the effects of unwanted variation.
Project consortium
The project brings together three leading European research and testing sites from the north of Scotland, England and Sweden in order to develop industry approved reliability testing practices. These practices will be applied by the research and testing sites, ensuring consistency and robustness of testing to demonstrate reliability across wave and tidal technologies.
The overall technical approach will be driven by SP Research, who bring their experience in reliability testing from the automotive industry. They will focus on developing framework methodologies that will be deployed at the onshore Offshore Renewable Energy Catapult test site in Blyth (England) and the European Marine Energy Centre’s offshore test sites in Orkney (Scotland).
Next steps: RiaSoR II
The goal of the RiaSoR project is to consistently learn from the physical interactions between the devices and their environments, while embedding this understanding and building robustness into marine energy technology designs. RiaSoR II is currently in development with the aim to implement the VMEA methodologies with a condition monitoring framework whereby more data from onshore and offshore testing of ocean energy devices validates VMEA analysis, and ultimately improves OPEX costs for wave and tidal developers.
Related press releases
- February 2016: Reliability in a Sea of Risk: developing a reliability testing culture for ocean energy
- October 2016: Free reliability methodology training workshop for marine energy
- December 2016: Ocean energy engineers discuss reliability in a sea of risk
- December 2016: Reliability guidance published for marine energy developers





